Paper Sizes
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Like systems of measurement, there have been many different paper size standards at different times and in different places.
Today there is one widespread metric international ISO standard for paper sizes. Standard paper sizes like ISO A4 are widely used all over the world. The ISO standard paper sizes are used for writing paper, stationery, cards, and some printed documents. The standards also have related sizes for envelopes. In North America, a local standard is used that is still based on imperial measurements.
[edit] A-series
The international A-series of paper sizes is now universally accepted as the standard used for all drawings, printed sheets and written materials. The A-series and B-series formats were designated ISO 216 in 1975, and are based on the German DIN (German Institute for Standardisation) 476 standard for paper sizes, which uses an aspect ratio of 1:√2.
[edit] History and adoption of the A-series.
The advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of √2 was first noted in 1786 by the German scientist and philosopher Georg Christoph Lichtenberg. During the First World War (1917), while working as a meteorologist on the Western front, Dr Walter Porstmann (German mathematician and engineer) published a work on standards which turned Lichtenberg's idea into a proper system of different paper sizes.
Dr. Walter Porstmann (1886-1959)
The published work came to the attention of Waldemar Hellmich, the first director of NADI (Standardisation Committee of German Industry) in 1917. In 1926 the organisation was renamed as DNA (German Standardisation Committee), and in 1975 it was renamed again as the German Institute for Standardisation, or 'DIN'.
(Note: The acronym, 'DIN,' is often incorrectly described as Deutsche Industrienorm ("German Industry Standard"). This is largely due to the historic origin of the DIN as "NADI". Indeed, NADI published their standards as DI-Norm (Deutsche Industrienorm). For example, the first published standard was 'DI-Norm 1' (relating to tapered pins) in 1918. Many people still mistakenly associate DIN with the old DI-Norm naming convention.)
On 18th August 1922 Porstmann's system new DIN standard (DIN 476) was launched, with the A-series and B-series replacing a vast variety of other paper formats. Even today the paper sizes are called "DIN A4" in everyday use in Germany and Austria. The term Lichtenberg ratio has recently been proposed for this paper aspect ratio.
The Lichtenberg Ratio (1: 1.4142) is occasionally confused with the Golden Ratio, which is 1: 1.618. While aesthetically pleasing properties have been attributed to both, the Lichtenberg Ratio has the advantage of preserving the aspect ratio when cutting a page into two. The Golden Ratio, on the other hand, preserves the aspect ratio when cutting a maximal square from the paper, a property is not particularly useful for office applications. The Golden Ratio was a very fashionable topic in antique and renaissance arts literature and it has a close connection to the Fibonacci sequence in mathematics. Many examples of the Golden ratio can be found in art and architecture.
The DIN 476 standard spread quickly to other countries.
| Germany (1922) |
| Belgium (1924) |
| Norway (1926) |
| Finland (1927) |
| Switzerland (1929) |
| Sweden (1930) |
| Soviet Union (now Russia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Latvia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Estonia and Lithuania) (1934) |
| Hungary (1938) |
| Italy (1939) |
| Uruguay (1942) |
| Argentina and Brazil (1943) |
| Spain (1947) |
| Austria and Iran (1948) |
| Romania (1949) |
| Japan (1951) |
| Denmark and Czechoslovakia (now Czech Republic and Slovakia) (1953) |
| Israel and Portugal (1954) |
| Yugoslavia (now Slovenia, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Kosovo and Bosnia-Herzegovina.) (1956) |
| India and Poland (1957) |
| United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland (1959) |
| Venezuela (1962) |
| New Zealand (1963) |
| Iceland (1964) |
| Mexico (1965) |
| South Africa (1966) |
| France, Peru and Turkey (1967) |
| Chile (1968) |
| Greece (1970) |
| Singapore and Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe) (1970) |
| Bangladesh (1972) |
| Thailand and Barbados (1973) |
| Australia and Ecuador (1974) |
| Colombia and Kuwait (1975) |
[edit] ISO 216
By 1975 so many countries were using the German system that it was established as an ISO standard (ISO 216) by the International Organisation for Standardisation, as well as the official document format for the United Nations.
In 1977, a large German car manufacturer performed a study of the paper formats found in their incoming international mail and concluded that out of 148 examined countries, 88 were already using the A series formats. Today the standard has been adopted by all countries in the world except the United States and Canada. In Mexico, Costa Rica, Colombia, Venezuela, Chile and the Philippines the US letter format is still in common use, despite their official adoption of the ISO standard.
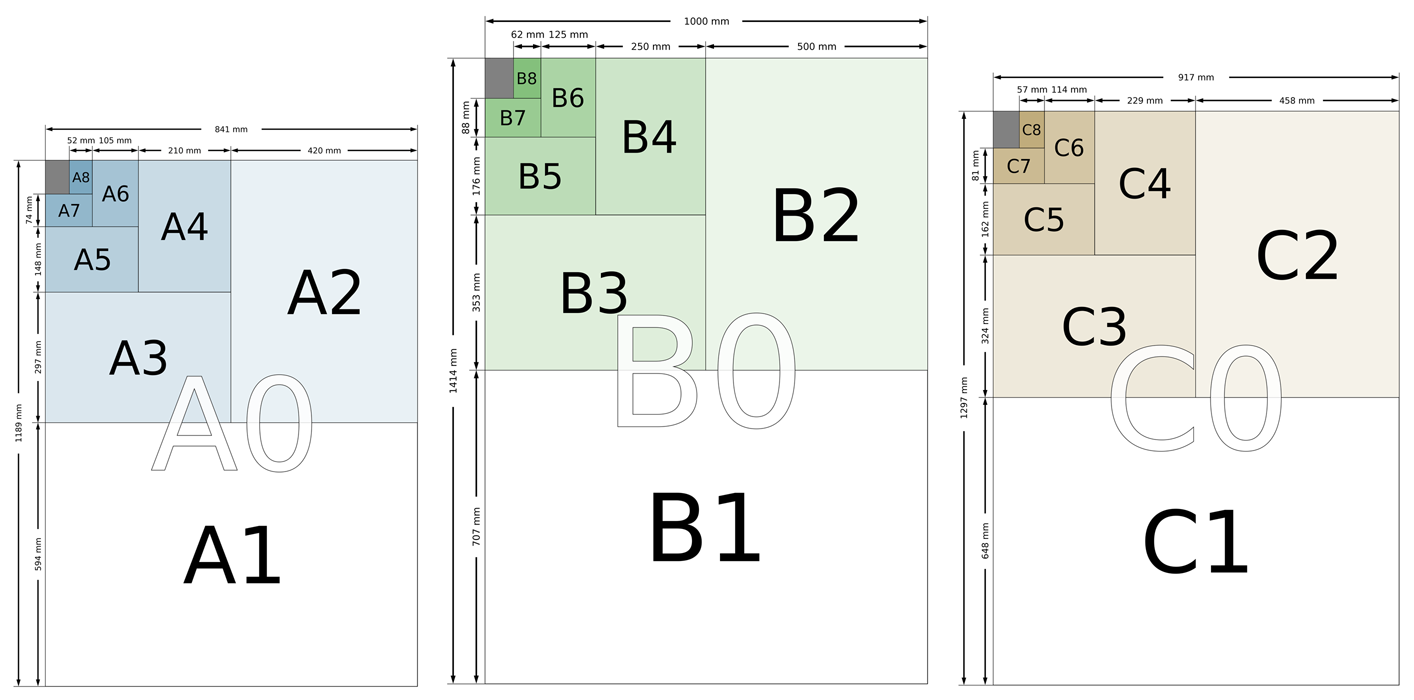
The ISO 216 standard defines the "A" and "B" series of paper sizes. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except DL) have the same aspect ratio of 1:√2.
ISO paper sizes (plus rounded inch values)
| Format | A series | B series | C series | |||
| Size | mm × mm | in × in | mm × mm | in × in | mm × mm | in × in |
| 0 | 841 × 1189 | 33.11 × 46.81 | 1000 × 1414 | 39.37 × 55.67 | 917 × 1297 | 36.10 × 51.06 |
| 1 | 594 × 841 | 23.39 × 33.11 | 707 × 1000 | 27.83 × 39.37 | 648 × 917 | 25.51 × 36.10 |
| 2 | 420 × 594 | 16.54 × 23.39 | 500 × 707 | 19.69 × 27.83 | 458 × 648 | 18.03 × 25.51 |
| 3 | 297 × 420 | 11.69 × 16.54 | 353 × 500 | 13.90 × 19.69 | 324 × 458 | 12.76 × 18.03 |
| 4 | 210 × 297 | 8.27 × 11.69 | 250 × 353 | 9.84 × 13.90 | 229 × 324 | 9.02 × 12.76 |
| 5 | 148.5 × 210 | 5.83 × 8.27 | 176 × 250 | 6.93 × 9.84 | 162 × 229 | 6.38 × 9.02 |
| 6 | 105 × 148.5 | 4.13 × 5.83 | 125 × 176 | 4.92 × 6.93 | 114 × 162 | 4.49 × 6.38 |
| 7 | 74 × 105 | 2.91 × 4.13 | 88 × 125 | 3.46 × 4.92 | 81 × 114 | 3.19 × 4.49 |
| 8 | 52 × 74 | 2.05 × 2.91 | 62 × 88 | 2.44 × 3.46 | 57 × 81 | 2.24 × 3.19 |
| 9 | 37 × 52 | 1.46 × 2.05 | 44 × 62 | 1.73 × 2.44 | 40 × 57 | 1.57 × 2.24 |
| 10 | 26 × 37 | 1.02 × 1.46 | 31 × 44 | 1.22 × 1.73 | 28 × 40 | 1.10 × 1.57 |
[edit] Sizes in the A-series
The A-series was derived from a rectangle piece of paper (A0) having an area of 1 m2, the length of whose sides are in the proportion 1:√2 (1: 1.4142).
The dimensions of this rectangle of paper (A0) is 1189 × 841 mm and by progressively halving the larger dimension, a reducing series of rectangles is produced, in which the proportions of the original rectangle remains relativity unchanged (at approximately 1:1.4142), and in which the area of each rectangle is half that of its predecessor in the series.
This system (as with the B-series and C-series) allows scaling without compromising the aspect ratio from one size to another – as provided by office photocopiers, e.g. enlarging A4 to A3 or reducing A3 to A4. Similarly, two sheets of A4 can be scaled down to fit exactly one A4 sheet without any cut-offs or margins.
[edit] Trimmed sizes and tolerances
The A formats are trimmed sizes and therefore exact; stubs of tear-off books, index tabs, etc. are always additional to the A dimensions. Printers purchase their paper in sizes allowing for the following tolerances of the trimmed sizes.
- For dimensions up to and including 150 mm (5.9 in), ±1 mm (0.04 in)
- For dimension greater than 150 mm up and including 600 mm (5.9 to 23.6 in), ±1.5 mm (0.06 in)
- For dimensions greater than 600 mm (23.6 in), ±2 mm (0.08 in).
[edit] Folding A sheets
Recommended methods of folding the larger A-sized prints are shown below.
[edit] Weights
Weights for the A-series are easy to calculate. A standard A4 sheet made from 80 g/m2 paper will weigh 5 g (as it is one 16th of an A0 page, measuring 1 m2), allowing one to easily compute the weight—and associated postage rate—by counting the number of sheets used.
[edit] German extensions
In the original German standard and specification of DIN 476 for the A and B sizes there are two other sizes that differ to their international successor:
DIN 476 provides an extension to formats larger than A0, denoted by a prefix factor. In particular, it lists the two formats 2A0, which is twice the area of A0, and 4A0, which is four times A0:
| DIN 476 overformats | ||
| Name | mm × mm | in × in |
| 4A0 | 1682 × 2378 | 66.22 × 93.62 |
| 2A0 | 1189 × 1682 | 46.81 × 66.22 |
[edit] B-series
The less common B Series of paper sizes were introduced to cover desirable sheet proportions that were not included by the prominent A Series. As with the A series, the lengths of the B series have the ratio 1:√2.
The area of B size sheets are the geometric mean of successive A-series sheets. For instance, the area of the B1 sheet (0.707 m²) is in between A0 (1 m²) and A1 (0.5 m²). The B Series is used for passports, envelopes and posters. B5 has become a conventional size for many books.
[edit] C-series (Envelope Sizes)
The entire C-series suite of envelopes are designed to hold their A-series’ counterparts, and are defined by ISO 269. The area of C series sheets is the geometric mean of the areas of the A and B series sheets of the same number. So, the area of a C4 sheet is the geometric mean of the areas of an A4 sheet and a B4 sheet.
For instance, a C4 envelope can hold a flat A4 sheet; a C5 can house a flat A5 sheet and so on, and C4 paper fits inside a B4 envelope, as well. The DL (Dimension Lengthwise) envelope was created to hold a concertina folded sheet of A4, or a standard sized compliments slip.
[edit] CAD usage
Computer Aided Design (CAD) uses these paper sizes too, with the addition on larger drawings of a gripping margin for the printer or plotter.
[edit] Technical drawing pen sizes
Technical drawing pens follow the same size-ratio principle. The standard sizes (m ISO) differ by a factor √2. These pens are: 2.00 mm, 1.40 mm, 1.00 mm, 0.70 mm, 0.50 mm, 0.35 mm, 0.25 mm, 0.18 mm and 0.13 mm.
So after drawing with a 0.35 mm pen on A3 paper and reducing it to A4, you can continue with the 0.25 mm pen. (ISO 9175-1). Other sizes of pens are available, however, to keep the same factor when working between different size sheets, the standard sizes of pens (m ISO) should be used.
[edit] Using non-standard sizes
The large differential between A0 and A1 has led to the introduction in some offices of a non-standard size sheet (referred to by magazine publishing as a “bastard size”) to reduce the gap, but the use of non-standard intermediate sizes is not desirable. These non-standard sizes have to be cut from paper of a larger size, and their non-standard proportion lead to difficulties in folding, storage and photographic reproduction.
[edit] Size management
Using non-standard sheets should always be avoided, and if an intermediate sizes are needed between A0 and A1 then the B1 size should be used instead. A0 can be incredibly cumbersome at times, both in the drawing office and on site, and on the whole it would seem to be preferable to set the A1 sheets as the upper limit for working drawings in all but the most exceptional circumstances, e.g. presentations, displays, etc. The site plan for even the largest of projects can usually be illustrated at the appropriate scale on an A1 sheet.
Apart from this upper limitation it is clearly sensible to restrict as far as possible the number of different sized drawings on any one project. An early appraisal of the size of the job and of the appropriate scale for the general arrangement planes will probably establish the format for the complete set of such drawings; normally it is not difficult to contrive that the assemblies and the ranges of component drawings should also be drawn on sheets of that size. The majority of the drawings in the average set therefore will appear in either A1 or A2 format, depending upon the size of the project.
The nature of sub-component drawings and schedules however, tends to make a smaller format more suitable, and there will always be a number of small details which it would be pointless to draw in one corner of an A1 sheet and which it would be confusing to attempt to collect together on a single sheet. The ‘miscellaneous details’ approach should never be used as it will lead to confusion between designer and builder.
Where the format for the other drawings is A2 it is probably worth wasting a little paper for the sake of obtaining a manageable set of consistent size. Where the general size is A1 however, a smaller sheet become necessary and whether this should be A4 or A3 is a matter for some debate.
[edit] Pros and cons of using A4 over A3
The advantages of the A4 format are:
- A substantial amount of the project information is already in A4 format-specification, bills of quantities, architect’s instructions, correspondence, etc.
- Trade literature is normally A4 and if you wish to include manufactures’ catalogues as part of your set then they are more readily absorbed into the structure of the set if you already have an A4 category.
- Most users (both producer and recipient) will have access to an A4 printer or photocopier with the facility that this offer to, for example, the contractor who wishes to get alternative quotes for a particular item and can rapidly produce a drawing. However, A3 copiers are very common in the home and in offices these days.
- The restricted size of sheets makes it more suitable for producing standard drawings, where it is necessary to limit the amount and extent of the information shown in order to preserve it ‘neutrality’.
- Architect’s instructions are frequently accompanied by a sketch detail and the A4 format simplifies filling and retrieval.
- A bound set of A4 drawings is suitable for shelf storage, unless you fold A3s in half. A3s are generally an inconvenient size to store, whether on a shelf, in a plan chest drawer, or in a vertifile. A4’s can also be carried around easily.
The disadvantages of the A4 format are:
- The drawing area is too small. One is constantly being forced into the position of limiting what is shown because these is just not room on the paper, or of selecting an inappropriately small scale.
- There is no room to record amendments adequately, or for that matter to incorporate a reasonably informative title panel.
- And finally, builders, especially when working on site, don’t like them. They would prefer the larger size of A3.
The choice is not easy, but on the whole most people would favour A3 as the smallest sheet of a set, if only for the pragmatic reason that you can, at a pinch, hang them landscape in a vertifile; that you can bind them into a specification or a bill of quantities and fold them double; that you can copy them in two halves on a photocopier and tape the two halves together; and that wasting paper is, in the last resort, cheaper than redrawing a detail which in the end would not quite go on the sheet.
[edit] Pre-metric paper sizes and North American paper users
(Note: There is a separate article on North American paper sizes on this Wiki)
Old drawings will frequently be found in the sizes common prior to the changeover to metric. These sizes are given in the table below.
| Name | in × in | mm × mm | Ratio |
| Emperor | 48 × 72 | 1219 × 1829 | 1.5 |
| Antiquarian | 31 × 53 | 787 × 1346 | 1.7097 |
| Grand eagle | 28.75 × 42 | 730 × 1067 | 1.4609 |
| Double elephant | 26.75 × 40 | 678 × 1016 | 1.4984 |
| Atlas* | 26 × 34 | 660 × 864 | 1.3077 |
| Colombier | 23.5 × 34.5 | 597 × 876 | 1.4681 |
| Double demy | 22.5 × 35.5 | 572 × 902 | 1.5(7) |
| Imperial* | 22 × 30 | 559 × 762 | 1.3636 |
| Half Imperial | 22 × 15 | 559 × 381 | 1.4672 |
| Double large post | 21 × 33 | 533 × 838 | 1.5713 |
| Elephant* | 23 × 28 | 584 × 711 | 1.2174 |
| Princess | 21.5 × 28 | 546 × 711 | 1.3023 |
| Cartridge | 21 × 26 | 533 × 660 | 1.2381 |
| Royal* | 20 × 25 | 508 × 635 | 1.25 |
| Sheet, half post | 19.5 × 23.5 | 495 × 597 | 1.2051 |
| Double post | 19 × 30.5 | 483 × 762 | 1.6052 |
| Super royal | 19 × 27 | 483 × 686 | 1.4203 |
| Medium* | 17.5 × 23 | 470 × 584 | 1.2425 |
| Demy* | 17.5 × 22.5 | 445 × 572 | 1.2857 |
| Large post | 16.5 × 21 | 419 × 533 | 1.(27) |
| Copy draught | 16 × 20 | 406 × 508 | 1.25 |
| Large post | 15.5 × 20 | 394 × 508 | 1.2903 |
| Post* | 15.5 × 19.25 | 394 × 489 | 1.2419 |
| Crown* | 15 × 20 | 381 × 508 | 1.(3) |
| Pinched post | 14.75 × 18.5 | 375 × 470 | 1.2533 |
| Foolscap* | 13.5 × 17 | 343 × 432 | 1.2593 |
| Small foolscap | 13.25 × 16.5 | 337 × 419 | 1.2453 |
| Brief | 13.5 × 16 | 343 × 406 | 1.1852 |
| Pott | 12.5 × 15 | 318 × 381 | 1.2 |
( * The sizes marked with an asterisk are still in use in the United States.)
[edit] Drawing boards
Drawing boards are currently manufactured to fit A-size paper, while vertical and horizontal filing cabinets and chests have internal dimensions approximately corresponding to the board sizes listed in the table below. Boards, cabinets and chests designed for pre-metric paper sizes are still in use.
| Type of board | Size | Width (mm) | Length (mm) |
| Parallel motion unit only or parallelogram type drafting machine | |||
| A2 | 470 | 650 | |
| A1 | 730 | 920 | |
| A0 | 920 | 1270 | |
| 2A0 | 1250 | 1750 | |
| Track or tolley type drafting machine requiring additional 'parking' area on one side. | |||
| A1 extended | 650 | 1100 | |
| A0 extended | 920 | 1500 | |
| Parallel motion unit with drafting head requiring additional 'parking' area at the bottom of the board. | |||
| A1 deep | 730 | 920 | |
| A0 deep | 1000 | 1270 |
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Architectural publishing.
- Architectural reprography.
- Brand guidelines.
- Concept drawing.
- Drawing board.
- Elevations.
- Manual drafting techniques.
- North American Paper Sizes
- Types of Drawings.
- Types of paper.
- Notation and symbols.
- Scale drawing.
- Standard hatching styles for drawings.
- Symbols on architectural drawings.
- Technical notes on architectural publishing.
- Writing technique.
Featured articles and news
Gregor Harvie argues that AI is state-sanctioned theft of IP.
Preserving, waterproofing and decorating buildings.
Many resources for visitors aswell as new features for members.
Using technology to empower communities
The Community data platform; capturing the DNA of a place and fostering participation, for better design.
Heat pump and wind turbine sound calculations for PDRs
MCS publish updated sound calculation standards for permitted development installations.
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.